As more fleets adopt electric standby for refrigerated trailers, one of the most important (and most overlooked) considerations is plug compatibility. The type of inlet on a TRU determines what it can safely plug into, what power it can accept, and whether it will work reliably across a mixed fleet.
Confusion often arises because containers, trailers, and box trucks all use different connection configurations, and not all connectors are interchangeable. Standardization is what keeps operations safe, efficient, and compliant, especially as electrification accelerates across the cold chain.
This guide breaks down the differences, what standardization actually means, and how operators can avoid costly compatibility issues.
Why Plug Compatibility Matters for eTRUs
Electric transport refrigeration units (eTRUs) rely on a dedicated power inlet that must match the electrical configuration of the equipment providing shore power. When an unstandardized or unrecognized connection type is used, facilities can risk:
- Unsafe electrical connections
- Incorrect grounding or phase alignment
- Equipment that cannot be powered
- Higher installation and maintenance costs, specially with expensive proprietary equipment
- Increased downtime
Standardization ensures that eTRUs across different makes and models can be powered safely and consistently.
Why Different Refrigerated Equipment Uses Different Plugs
This occurs when a trailer first connects to shore power and must pull the temperature of the trailer down to the required temp.
Although refrigerated containers, box trucks, and trailer TRUs all rely on electric power, they do not use the same connector. Each type of equipment is designed with its own electrical configuration, ensuring it can only be connected to the appropriate power source.
This matters because it prevents equipment from being plugged into a circuit with the wrong voltage, amp, or configuration.
Refrigerated Containers
Containers use IEC 60309 connectors, but with different ratings and configurations than trailer TRUs. Even if they look similar, they are not compatible, which prevents incorrect use.
Box Trucks
Many box trucks operate on 50A, 240V systems. These require their own dedicated infrastructure or a specialized unit that can deliver both 480V and 240V, but typically cannot connect to the receptacles used for trailer electric standby.
These differences are intentional. They help keep equipment protected and ensure that only properly matched systems are connected.
Avoiding Proprietary Plug Systems
OncWhile standardized IEC connectors support consistent, cross-fleet compatibility, some systems use proprietary multi-pin connectors, including 6-pin variations. These require specialized parts, limit compatibility, and increase long-term cost compared to standardized configurations.
Choosing non-proprietary connectors keeps operations flexible and supports mixed fleets without tying facilities to a single supplier or hardware ecosystem.
Want a deeper technical look at plug types,
OEM compatibility, and electrification planning?
Explore our eTRU Webinar Series
How ESL Supports Standardized, Non-Proprietary Operation
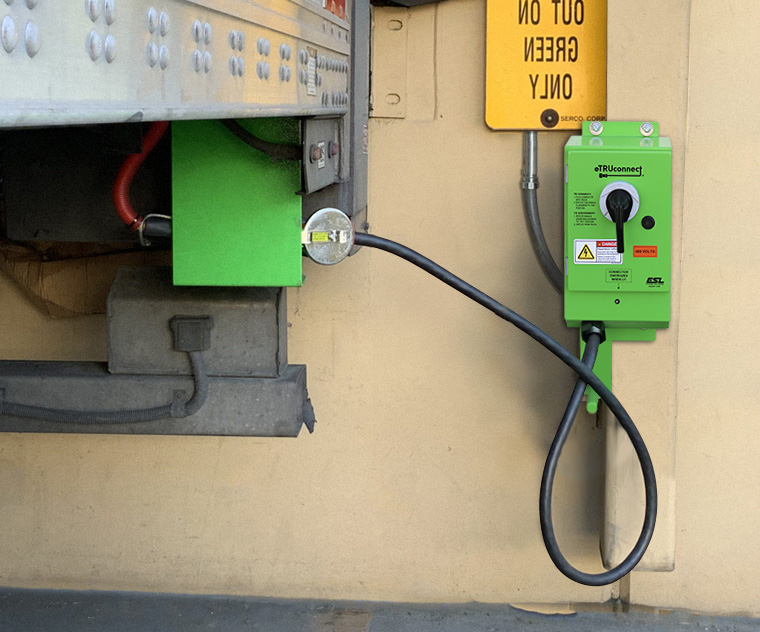
ESL’s eTRUconnect® system is built around the standard IEC 60309 trailer connector, ensuring compatibility with electric-standby-equipped TRUs across major OEMs.
Key advantages include:
- Universal TRU compatibility using standardized IEC connectors
- Safety-interlocked design that cuts power during disconnect
- Integrated branch-circuit protection for safe operation
- Durable, outdoor-rated construction for harsh yard environments
- Dual drive-off protection to prevent equipment damage
This standardized, non-proprietary approach ensures facilities can electrify confidently and support mixed fleets without costly customization.
Planning eTRU Shore Power Infrastructure With Compatibility in Mind
Not every trailer operates at peak load simultaneously. Most facilities see a predictable mix:
Choosing standardized IEC trailer connectors provides clear benefits when expanding or upgrading electric standby infrastructure:
- Cross-Fleet Flexibility
Any trailer with a standard IEC inlet can connect to any compatible position. - Operational Simplicity
A single connector type reduces training needs and minimizes operator errors. - Lower Total Cost of Ownership
Standard parts minimize long-term maintenance and replacement costs. - Future-Ready Design
As fleets evolve, standardized connectors ensure new equipment remains compatible.
Why Standardization Is the Smartest Path Forward
Standardizing around IEC 60309 connectors provides a safe, scalable foundation for electric TRU adoption. Using a widely supported, non-proprietary connection system gives facilities the flexibility to support mixed fleets, adapt as equipment evolves, and protect their infrastructure investment.
Whether electrifying a few positions or an entire yard, standardization keeps operations reliable and future-ready.
Ready to Simplify Electrification for Your Fleet?
Let’s talk through your goals and determine what infrastructure approach makes the most sense for your facility.