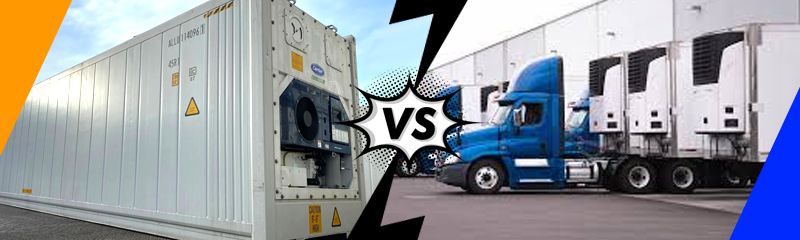
Generic terms like reefer, van, or freezer are often used to describe a variety of refrigerated equipment, but each type can have different electrical requirements. To ensure we quote the correct product, it’s important to understand exactly what kind of equipment will be plugged in.
Reefer Containers: The Ocean and Intermodal Workhorses
Reefer containers are typically used for ocean or intermodal shipping and come with a built-in cord and a male pin-and-sleeve plug, usually 440/480V 3-phase, 32A (IEC 60309). These cords are often visible coiled in a tray or hook on the container’s side. The container itself is a self-contained metal unit, similar in appearance to a standard shipping container, often 20 or 40 feet long.
Electric Transport Refrigeration Units (eTRUs): The Overland Option
Electric Transport Refrigeration Units (eTRUs), on the other hand, are usually mounted on trailers or trucks. Instead of a cord, they are equipped with a male inlet mounted on the unit’s exterior. The cord with the female connector is provided at the power source (dock, pedestal, or building).
Visually, eTRUs blend into the body of the trailer or appear as nose-mounted units on the front wall. At first glance, they may look like conventional diesel-powered TRUs, but the giveaway is the small inlet plate or recessed power port replacing the familiar fuel tank.
Quick visual differences:
- Reefer Containers: Large, box-like units with a coiled power cord and male plug. Often have corner castings for stacking/shipping.
- eTRUs: Mounted on trailers, often with no external cord. Look for an inlet plate or recessed power port on the side or front of the unit.
Why This Matters for Electrical Quotes
It’s important to note that not all containers or eTRUs use the same standard configuration. Some may have non-standard connectors or voltages depending on origin, manufacturer, or retrofit. Since pricing and product selection can vary significantly depending on the required connector or receptacle, confirming the exact electrical configuration — including voltage, phase, amperage, and plug type — helps avoid misunderstandings and ensures a safe, cost-effective solution.
Photos of the connection point, nameplate data, or equipment specifications are very helpful in making the correct selection.
If you’re looking for further assistance or ready for a project quote, Contact our team now!