Traditionally, Rubber Tire Gantries (RTGs) have been operated by diesel fuel. However, with the rising cost of fuel there has been a shift toward running RTGs on electrical power. In addition to reduced emissions, utilizing Electrified Rubber Tire Gantries can reduce fuel consumption by as much as 95% according to a recent article published by World Cargo News. Many ports that have implemented ERTGs are seeing a decrease in maintenance expenditures around 30% less than those that are fuel operated. Additional savings have also been reported on operating costs and communication/monitoring data systems. A shift toward this proven and reliable electrical system has been seen more and more in new ports across the world.
Whether a new port is looking to incorporate an Electrified Rubber Tire Gantry system in the design or an existing port is evaluating a retrofit, the following aspects should be considered in determining a safe and convenient means to connect and disconnect ERTGs:
What are the advantages of using a cable reel system versus bus bar system?
- Obstructions in the container terminal are reduced
- Allows for more flexibility in the terminal layout
- Collision risks with energized structures are minimized
- Decreases chances of electric shock
What are the advantages of utilizing a medium-voltage (MV) system over low-voltage (LV)?
- Lighter cable can be used
- Longer cable runs from the Electrified Rubber Tire Gantry connect/disconnect point to the RTG
- Electrical losses are minimized
- Accommodates the ability to daisy-chain several connection points, thereby minimizing cable runs from the substation to connect/disconnect points
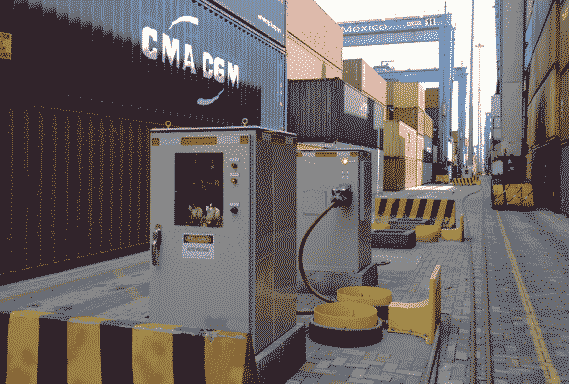
Making Safe Connections to ERTGs
ESL Power Systems, Inc.‘s ERTG Safety-interlocked Disconnect Cabinet provides connection points for ERTGs operating at medium-voltage. This system enables 4-6 RTGs to run from a single 4160V circuit by daisy-chaining the ERTG Disconnect Cabinet and stepping down the voltage on the RTG. This type of system is a more efficient option as it allows a smaller diameter cable to be used, thereby minimizing the footprint and obstructions of required equipment. In addition, the ERTG safety-interlock design features a 7.2kV push/pull receptacle, a medium voltage switch, and a mechanically interlocked ground switch. This safety-interlock system ensures a single RTG cable can be safely disconnected without tripping the upstream breaker and disrupting power supply to other RTGs.
To get an idea of how to operate an ERTG Safety-interlocked Disconnect Cabinet, please check out this ERTG Disconnect Cabinet Video.

