Those who have plugged in Refrigerated Containers (a.k.a “reefers”) know firsthand that water intrusion can cause reefer plugs and connectors to explode. This is extremely dangerous and can result in injury to the operator, damage to the plug, receptacle, and surrounding equipment. And obviously, the refrigerated cargo is no longer being cooled. Experienced operators will even shake the plug prior to plugging in; if they suspect water is inside they know better than to energize the plug.
Read morereefer/intermodal
Designing a Safe Reefer Connection: Part 1
Safe reefer operations require a receptacle system that exceeds minimum standards in electrical codes.

Safely connecting and disconnecting reefer containers operating on 3 Phase 440-480v power represents one of the largest safety risks from an electrical hazard at the majority of container terminals. Reefer receptacles are designed and listed to electrical safety standards of UL and CE self-certification, but these only “certify” that the receptacle can carry the required electrical load. Other standards, such as IEC 60309-1 and 60309-2 cover configurations of the plug and receptacle and ensure compatibility. It is widely accepted that dealing with 480v, 32A supply presents a safety (and liability) risk and that the standard is to have interlocked connections. A safety interlock is a mechanical or electrical device that prevents a receptacle from being energized unless the male plug is properly engaged and disconnects the power supply automatically as the plug is removed. Although the safety interlock design prevents operators from “making” or “breaking” under load, it is not required under electrical codes and in some cases, terminal construction contractors look to install non-interlocked receptacles, which pose a higher safety risk to operators, but offer cost savings. Some situations arise where contractors facing strict budgets try to install non-interlocked receptacles. The objective is to make sure interlocked receptacles rather than “complying” receptacles are specified when projects are tendered. As far as the design of the interlock is concerned, there are several options. ESL’s standard system detects the ground pin of the male plug before allowing the unit to be energized, whereas other designs interlock off the key on the side of the plug. ESL believes the ground pin is the safer option. Additionally, in some markets, plug keys are frequently “shaved off” to allow a 32A plug to mate with a 30A (non-interlocking) receptacle, meaning the 32A male plug must be replaced elsewhere in the supply chain in order to safely connect to a receptacle that interlocks at the key.
Operating Efficiently
Another important aspect of reefer power supply is designing the receptacle system so the terminal can perform reefer operations efficiently. In considering the layout of the reefer area(s), terminal management has to weigh the initial costs of installing more reefer outlet assemblies (ROAs) against the labor costs of managing cabling from fewer centralized ROAs. A reefer rack structure is typically six or seven containers wide and some operators opt for an ROA with six or seven receptacles mounted centrally. This configuration is more prone to tangled reefer cables, which present tripping hazards and the chance of disconnecting the wrong cable. Terminals with wider reefer racks may even require extension cables to reach the outer containers. Installing more receptacles per ROA is ultimately a cheaper solution, but a trend towards two and three-gang ROAs due to operational efficiencies is growing. Demand is also increasing for two LED lights, one to indicate line power is available to the ROA and a second to show that the receptacle is energized and power is flowing. If the first LED is not showing, the operator will know immediately that there is an upstream power supply problem. An available option is the incorporation of an equipment ground fault protection (GFP) device on an outlet module to isolate the effect of a phase to ground short. ESL has frequently been asked to incorporate a simple ground fault protection device that can isolate a fault at the receptacle and prevent upstream switch gear from being tripped by a short. Terminal design engineers need to take into account that reefers generate ground currents during the defrost cycle, so the GFP devices should be selected and set at a value above the defrost cycle ground currents to avoid nuisance tripping.
Read part 2 of our series focusing on reefer receptacle safety and damage control.
Introducing the New Q: ESL’s Latest Innovation
Safety, Value, Quality, and Innovation have played a key role in making ESL a worldwide industry leader in the design and manufacturing of safety-interlocked power outlets for refrigerated ISO containers. With this continuing mission in mind, ESL’s new Q module provides unparalleled safety and incorporates additional advances such as high visibility indicating light and extensive cycle testing for increased product reliability.
Watch ESL’s Q Module demo video to learn how we continuously stay ahead of product safety innovations.
Intermodal Infographic
ESL’s newest intermodal info-graphic highlights various reefer outlet assemblies (ROAs).. Learn about your options for powering refrigerated ISO containers.
Learn more about ESL’s capabilities and download standard specifications at: http://eslpwr.com/intermodal-reefer
ESL On The Move – 2016 Trade Show Recap
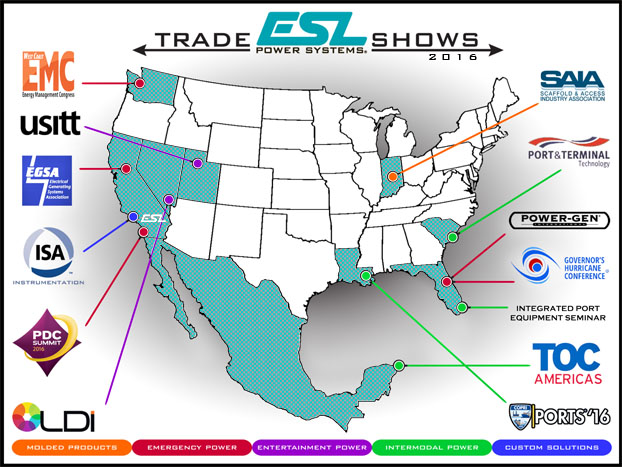
In 2016 ESL Power Systems attended over a dozen trade shows across the United States and internationally. Our journey included exhibiting at shows in many different regions geared towards multiple industries served including Intermodal Power, Molded Products, Custom Solutions, Entertainment Power and Emergency Power. ESL‘s expansive participation in industry leading conferences is illustrated on the map above.
| Instrumentation (Carson, CA) |
ASCE Ports
(New Orleans, LA) |
TOC Americas
(Cancun, MX) |
|---|---|---|
| USITT (Salt Lake City, UT) |
West Coast Energy Management Congress (Seattle, WA) |
Integrated Port Equipment Seminar (Miami, FL) |
| PDC Summit (San Diego, CA) |
SAIA (Indianapolis, IN) |
LDI (Las Vegas, NV) |
| Port & Terminal Technology (Charleston, NC) | EGSA – Fall Conference (Sacramento, CA) |
|
| Governor’s Hurricane Conference (Orlando, FL) | POWER-GEN International (Orlando, FL) |
Notable highlights from these shows include:
- ESL assisted with hosting the inaugural Integrated Port Equipment Seminars in Miami, FL. ESL collaborated with TMEIC, Phoenix Terminal Solutions, BROMMA, RTE, Remprex and Conductix to create a seminar focused on educating attendees on container operations of the future
- Promoting ESL’s new Molded Product Line at the SAIA Show in Indianapolis, IN
- First public display of ESL’s UL/cUL 1008 Listed 3200A TempTap -Generator Docking Station at POWERGEN International
To see where ESL will land next, visit our trade show page. For more information on any of our products please contact sales@eslpwr.com.

